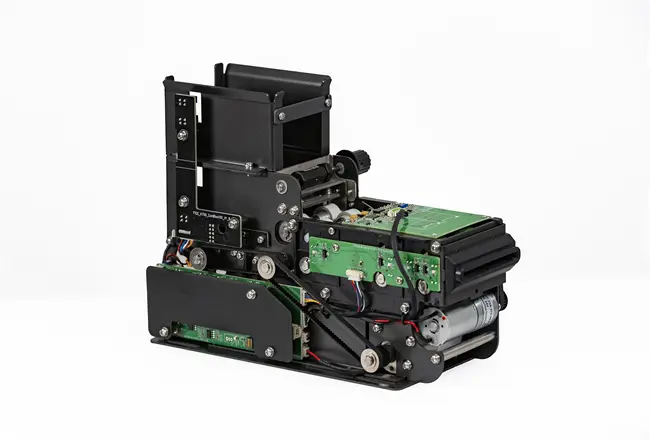
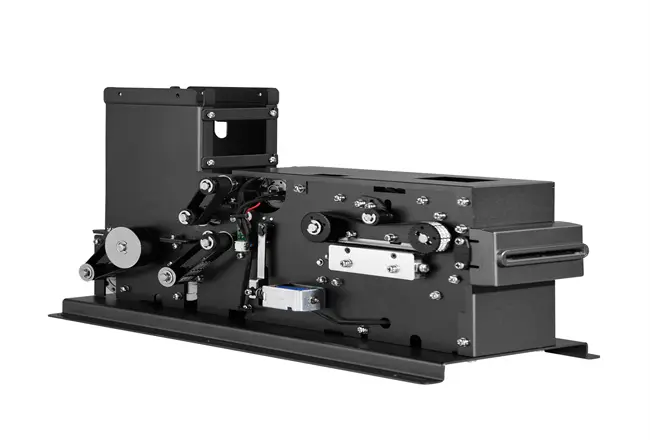
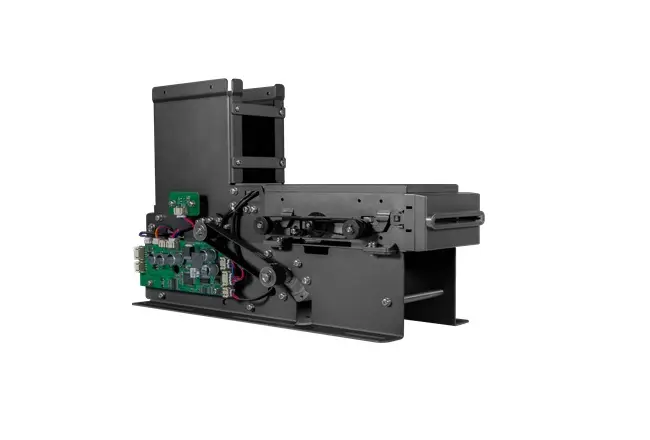
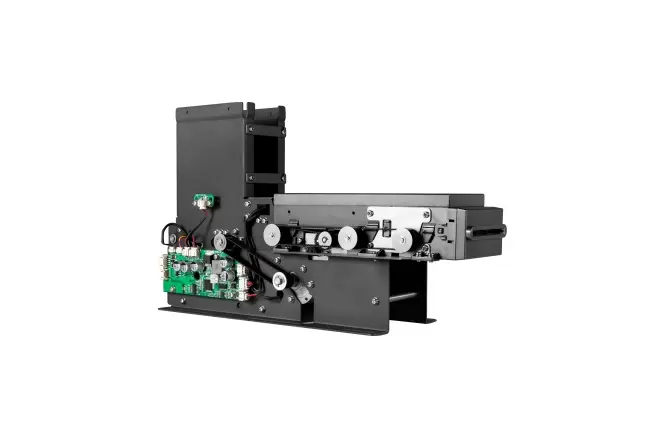
Related Post
How Does an SD Card Reader Writer Work and Best Practices?
2025-03-06SD (Secure Digital) card reader-writers are essential tools for transferring, storing, and managing digital data across multiple devices. They are widely used in cameras, smartphones, tablets, laptops, gaming consoles, and other electronic devices. These small yet powerful devices enable users to read and write data to SD cards efficiently, making them indispensable in modern digital workflows.
But how exactly does an SD card reader-writer work? In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the functionality, types, working mechanisms, and applications of SD card readers and writers. Additionally, we will discuss security considerations, troubleshooting techniques, and best practices for maintaining these devices.
What is an SD Card Reader Writer?
An SD card reader-writer is a device that allows users to read data from and write data onto an SD card. These devices function as a bridge between an SD card and a computer, smartphone, or other electronic devices. Some devices come with built-in SD card slots, while others require external SD card readers connected via USB or other interfaces.
Functions of an SD Card Reader Writer
- Reading Data: Extracting files, images, videos, and documents from an SD card.
- Writing Data: Copying or transferring new data to an SD card.
- Formatting SD Cards: Preparing an SD card for use by erasing all existing data and setting a new file system.
- Repairing Corrupted SD Cards: Some advanced SD card reader-writers can help recover lost or damaged files.

How Does an SD Card Reader Writer Work?
1. Data Communication Process
An SD card reader writer works by establishing a connection between the SD card and the device, allowing data transfer through electrical signals.
Steps in Data Transfer:
- Insertion of SD Card: The user inserts the SD card into the reader.
- Device Recognition: The reader detects the card and establishes communication with the host device (e.g., computer, camera, or smartphone).
- Reading Data: The reader retrieves stored data by interpreting the file system on the SD card.
- Writing Data: When files are copied or saved onto the SD card, the writer encodes the data onto the card’s storage sectors.
- Data Transfer Completion: Once the process is complete, the card can be safely removed from the reader.
2. File System and Formatting
SD cards use different file systems depending on their capacity and compatibility requirements:
- FAT32 – Common for SD cards up to 32GB; widely compatible but has a 4GB file size limit.
- exFAT – Suitable for SDXC (Extended Capacity) cards larger than 32GB, supports larger file sizes.
- NTFS – Used in Windows environments but less common for SD cards.
3. Power and Signal Processing
SD card readers use electronic circuits to convert analog signals into digital data. The reader supplies power to the SD card while facilitating two-way communication for reading and writing operations.
4. Secure Data Transfer Protocols
Some SD card readers employ UHS (Ultra High Speed) or USB 3.0/3.1 interfaces to ensure faster data transfers while maintaining security against data corruption or loss.
Types of SD Card Readers Writers
1. Built-in SD Card Readers
Many laptops and computers come with built-in SD card slots for direct reading and writing operations.
Advantages:
- No need for external devices.
- Direct and fast data transfer.
2. External USB SD Card Readers
External SD card readers connect to a device via USB, offering compatibility across multiple platforms.
Advantages:
- Portable and easy to use.
- Can support multiple SD card formats (SD, microSD, SDXC, etc.).
- Higher transfer speeds with USB 3.0 or USB-C models.
3. Wireless SD Card Readers
These advanced SD card readers enable wireless file transfer between SD cards and devices using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity.
Advantages:
- No physical connection required.
- Useful for mobile and remote applications.
4. Multi-Card Readers
These devices support multiple types of memory cards, including SD, microSD, CompactFlash, and Memory Stick.
Advantages:
- Versatile and supports various storage formats.
- Ideal for professionals handling different card types.
Applications of SD Card Reader Writers
1. Photography and Videography
- Used by professionals to transfer high-resolution images and videos from cameras to computers.
- Enables quick backup and editing workflows.
2. Mobile Storage Expansion
Smartphones and tablets use SD card readers to expand storage and transfer files.
3. Gaming Consoles and Entertainment Devices
Gaming systems utilize SD cards for game saves, software updates, and additional content storage.
4. Industrial and Security Systems
Used in surveillance cameras and industrial equipment for data logging and secure file storage.
5. Automotive and Navigation Systems
GPS devices and car multimedia systems rely on SD cards to store maps, software updates, and multimedia files.
Security and Data Protection Considerations
1. Protecting Against Data Corruption
- Always eject SD cards safely before removing them.
- Avoid using SD cards in multiple devices without formatting.
2. Encryption and Data Security
- Some SD card readers support hardware-based encryption to protect sensitive information.
- Password protection prevents unauthorized access.
3. Preventing Physical Damage
- Store SD cards in protective cases to prevent dust, moisture, and static damage.
- Avoid exposing SD card readers to excessive heat or cold.
Troubleshooting Common SD Card Reader Writer Issues
1. SD Card Not Recognized
- Ensure the SD card is properly inserted.
- Try using a different USB port or reader.
- Check for driver updates on your computer.
2. Slow Data Transfer Speeds
- Use high-speed SD cards with UHS support.
- Ensure the card reader supports USB 3.0 or 3.1 for faster performance.
3. Data Corruption or Loss
- Use data recovery software to retrieve lost files.
- Format the SD card properly before reusing it.
Best Practices for Using SD Card Readers Writers
1. Keep the Reader and SD Card Clean: Regularly clean the card slot and SD card contacts to prevent dust accumulation.
2. Use Compatible SD Cards: Always check the compatibility of your SD card with the reader.
3. Regularly Backup Important Data: Avoid data loss by frequently backing up files to a secondary storage device.
4. Update Drivers and Firmware: Keeping your SD card reader drivers up to date ensures proper functionality and security.
An SD card reader-writer is a critical tool for handling digital data efficiently. Whether you’re a photographer, gamer, or everyday user, understanding how these devices work helps in optimizing performance and preventing data loss. By following best practices and staying updated with emerging technologies, you can ensure secure and seamless data transfers for years to come.