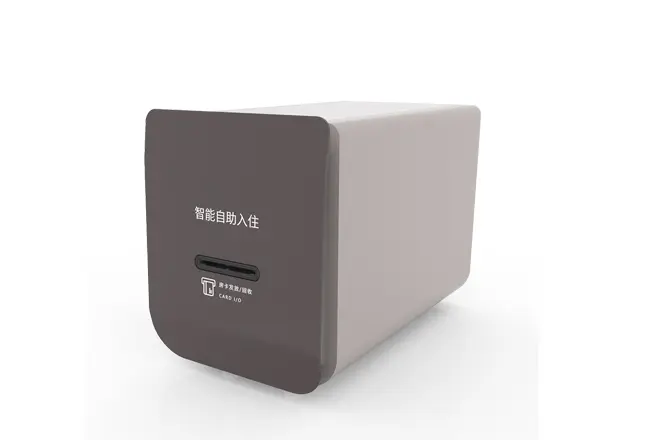
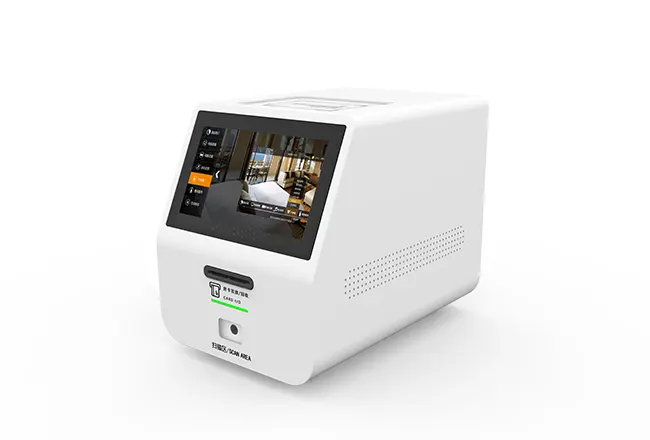
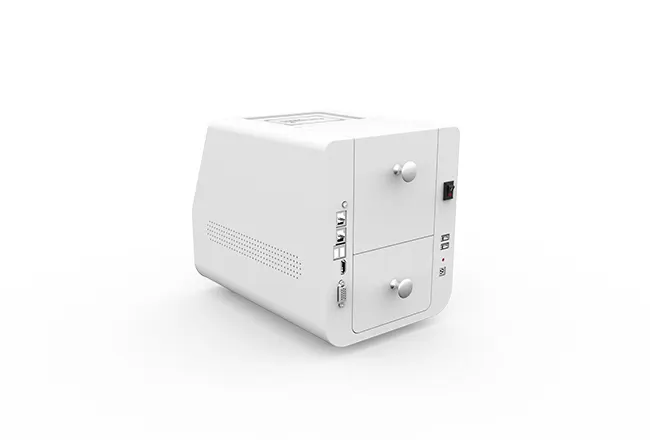
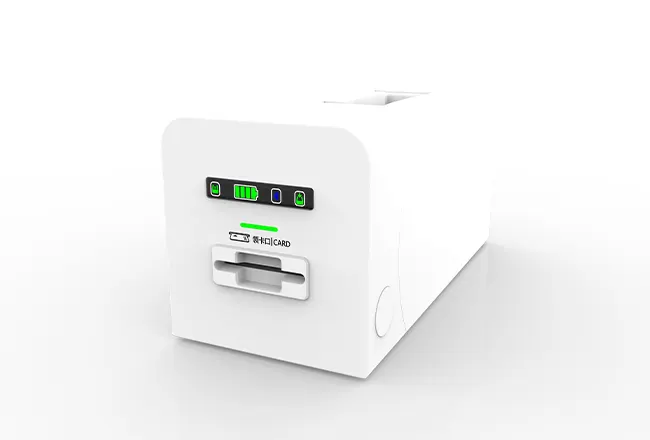
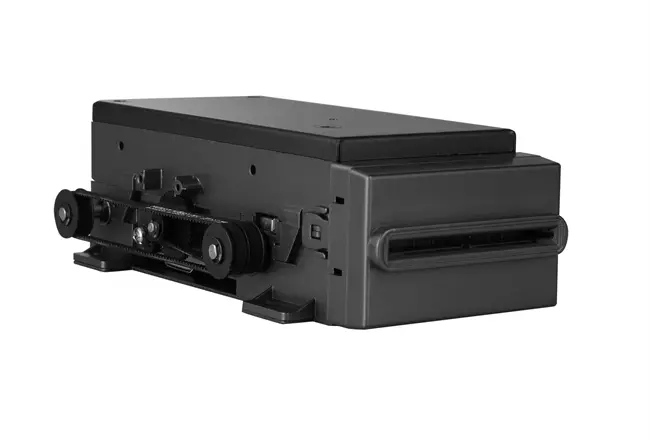
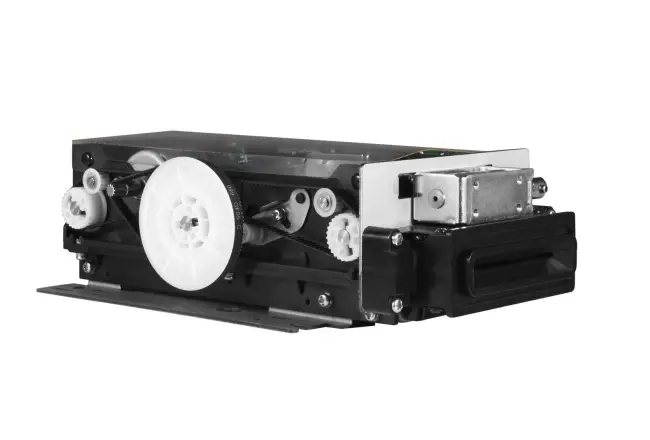
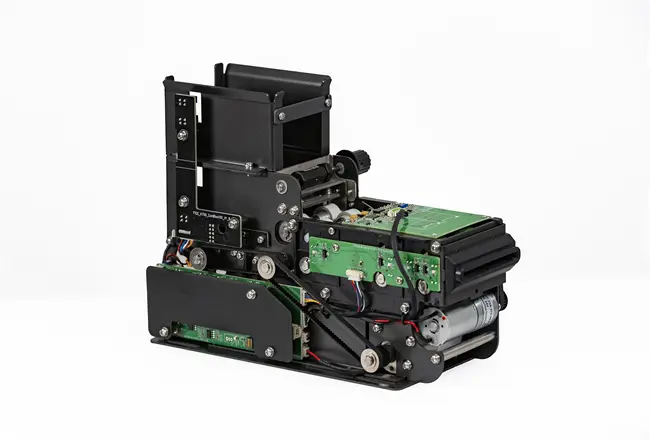
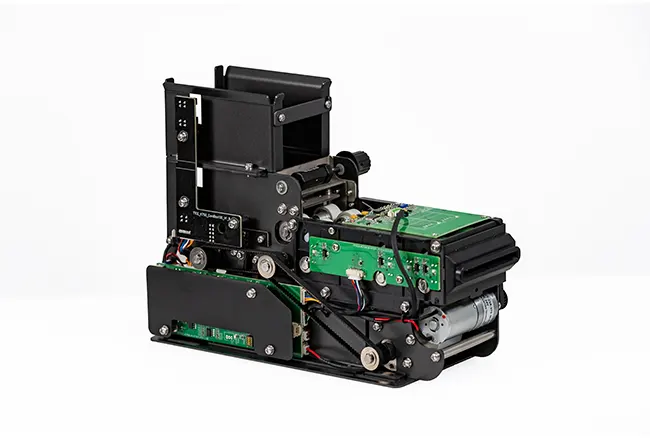
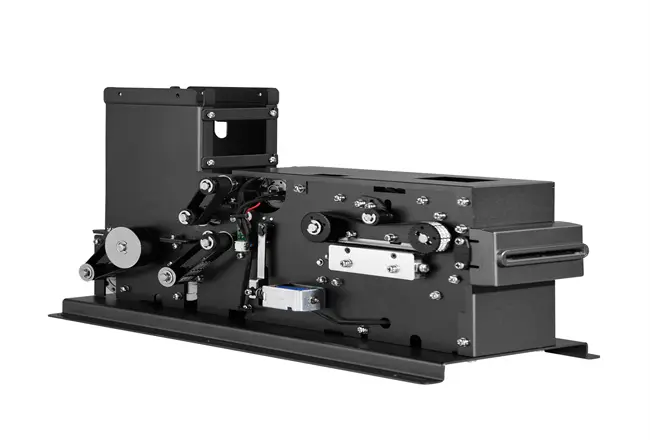
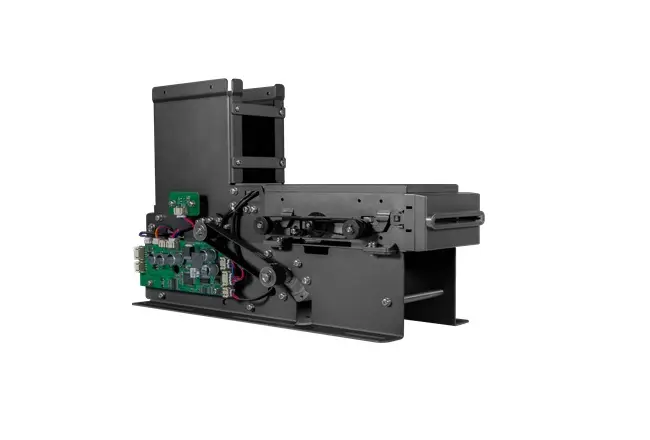
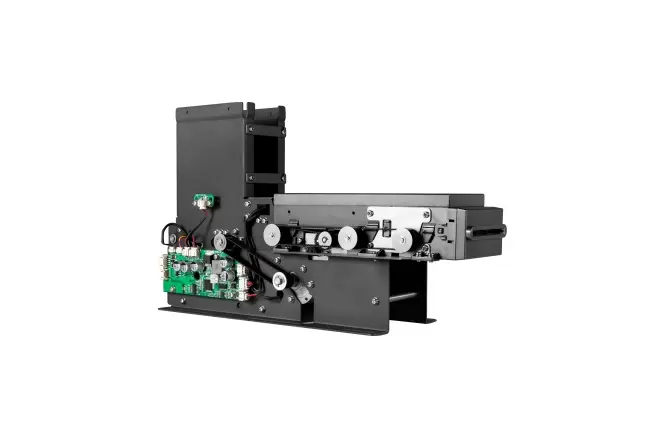
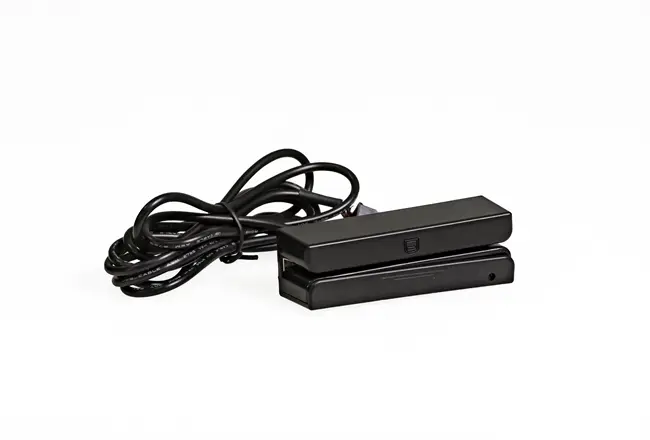
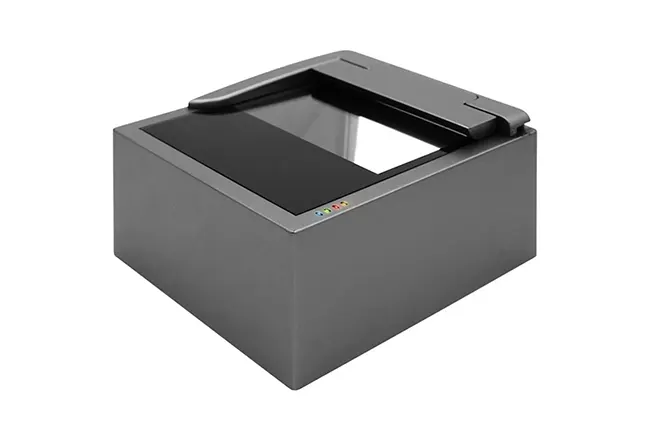
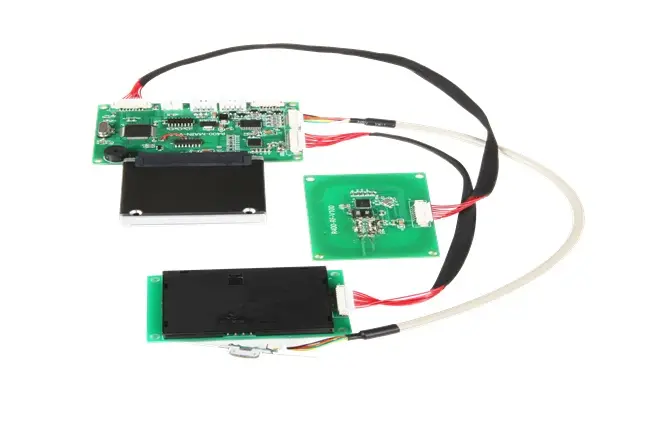
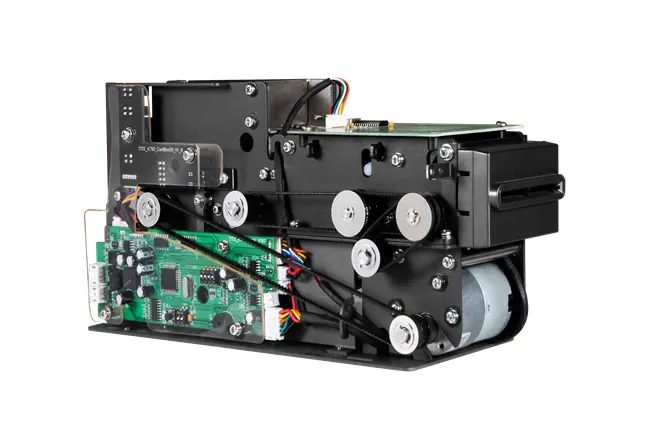
Circular Card Dispenser TTCE-K750-G
Recycle Hotel Room Key Card Dispenser With RFID Card Reader & Writer
- Small and exquisite design for easy integration into slim chassis or desktop terminals;
- Our machine adjusts itself to deliver stable performance in both card pick-up and drop-off tasks.
- The system includes sensors arranged correctly to show and tell machine status accurately.
- The chip reader technology in the systems support standard M1 cards out of the box.
- Supports cards of different thicknesses
Features of TTCE-K750-G
- Enhanced Circular Card Dispenser model now handles different card types especially those deformed materials.
- The K750-H can read and write cards that follow ISO1443A and ISO15693 standards.
- Setting the cassette automatically adjusts to maintain proper card collection and distribution functions.
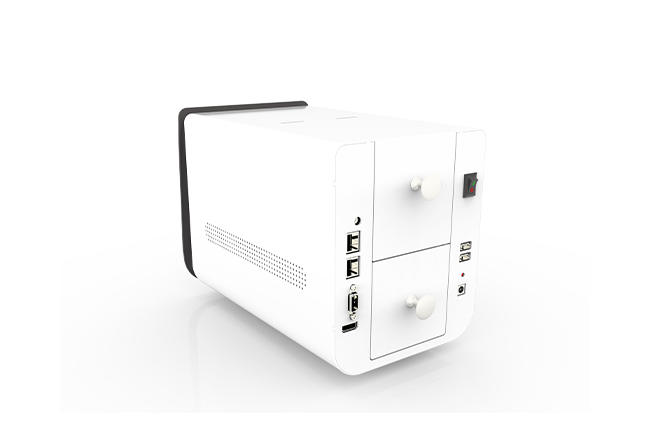
- RS232 Interface Connectivity: Enables seamless system integration.
- Compact & Space-Saving Design: Ideal for slim chassis and desktop terminals.
Details of TTCE-K750-G
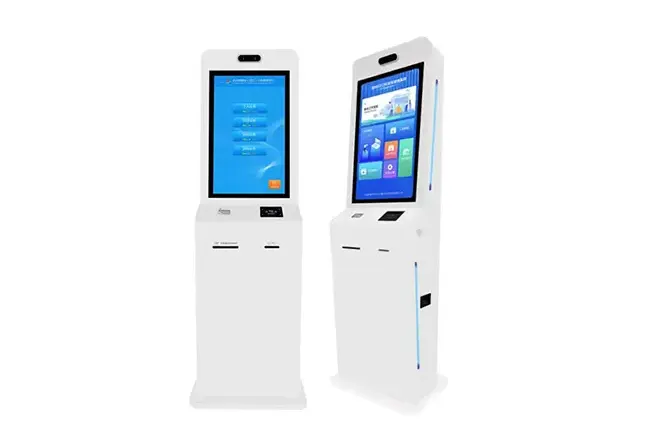
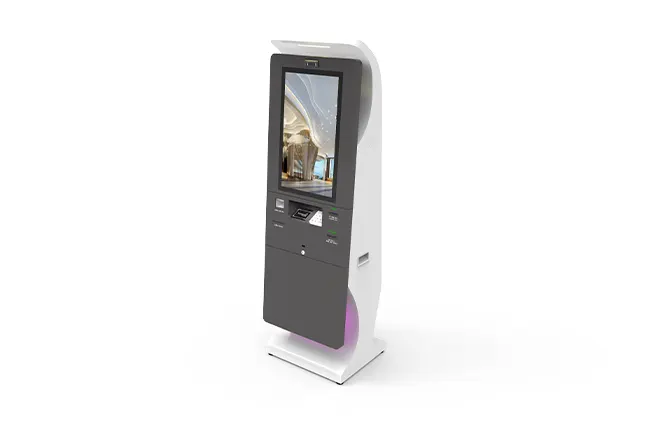
The K750-H Circular Card Dispenser improves on the K750-B model to handle hotel key card creation and waste material handling processes. The advanced device reads and writes RFID cards to enable efficient hotel guest registration and security measures. The improved card handling features let the device distribute cards without problems in busy public areas including hotels and self-service kiosks.
Specification of TTCE-K750-G
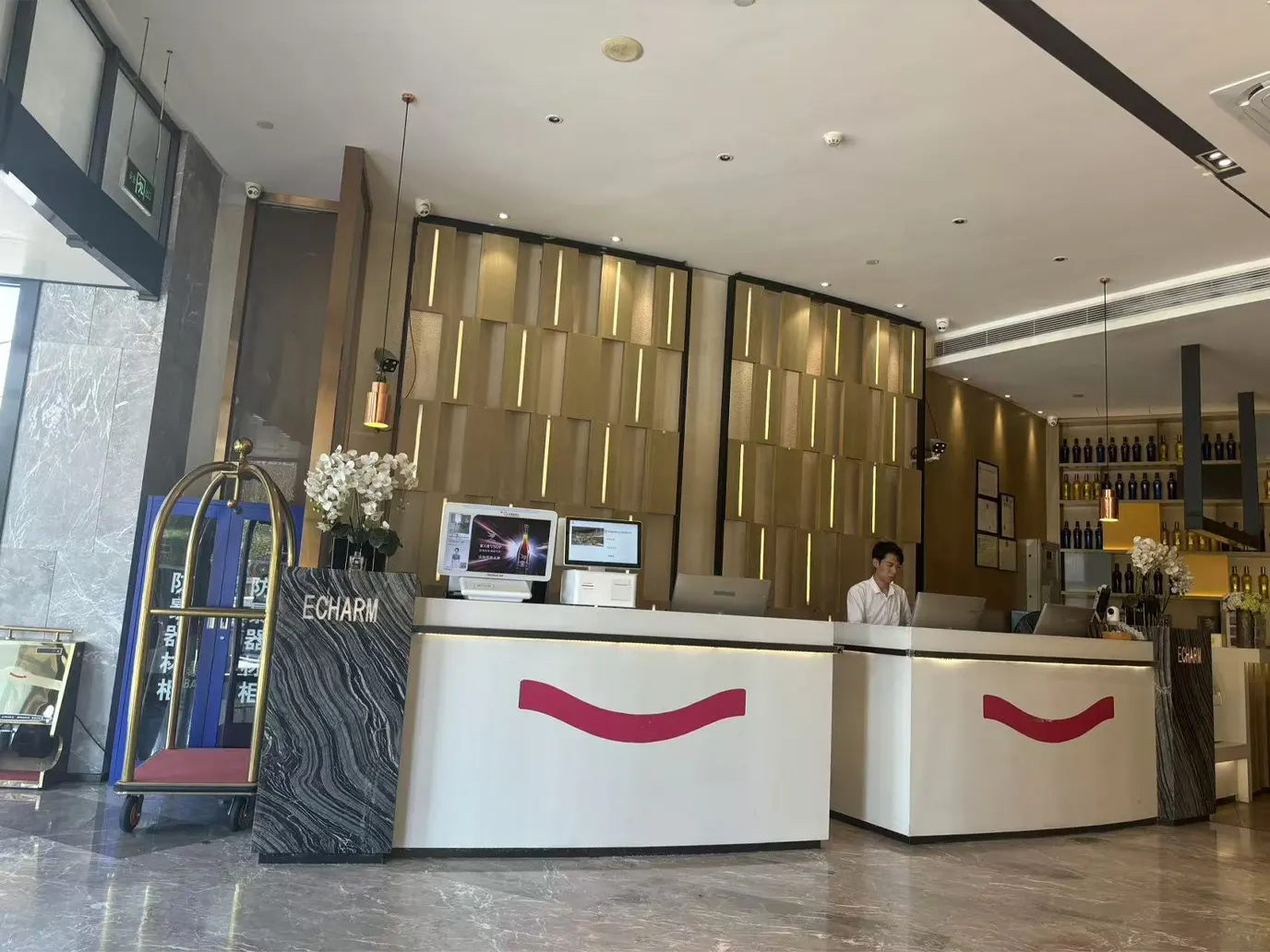
Hotels use the K750-H device to provide automatic room key card services that make guest check-in easier. Access control systems depend on this method to verify users with RFID-based authentication systems across multiple organization spaces. K750-H supports quick handling operations between stations to transport transportation tickets. The K750-H helps retail programs and loyalty programs make membership cards better while parking facilities handle automated entry and exit at the same time.
| Card Type | Contactless card: ISO/IEC 14443 15693 Type A & Type B Support mifare 1 S50, S70, UL card, mifare plus, mifare desfire |
| Card Specification | Material: Paper card and PC card Width: 54 ± 0.5 mm(W) Length: 85 ± 0.5 mm Thickness: 0.7 ~1.0mm |
| Power Supply | DC24V |
| Working Current | Idle: <100mA Peak: <2000mA |
| Interface | RS232 |
| Card hopper Capacity | 50 pcs standard cards at thickness of 0.76mm (Note: stacker capacity can be extended to 100pcs or 150pcs) |
| Alert Lamp | Card entry alert Few card alert Power on alert |
| Environmental Conditions | Operation temp: 0℃ to 50℃ Operation humi: 30~90% (relative humidity) |
| Life time | Drive parts: 500,000cycles |
| Certified | |
| Weight | About 2.0kg |
Application of TTCE-K750-G

Our Advantages
With an experienced R&D team, We can satisfy the diverse customization needs of our customers.

Expert Team and Customized Services
Our professional team excels in collaboration, delivering high-quality results while offering customized solutions to meet each customer’s unique needs and specifications.
Comprehensive One-stop Solution
We provide a complete package, from initial manufacturing to ongoing support, including tailored ODM and OEM services, ensuring a seamless experience.

Global Export Experience
With 23 years of development, our modules are exported worldwide, bringing extensive market insights and customer experience across global markets.
Contact Us

Online Message
For a faster response, you can contact via phone or WhatsApp: +86 18926404886 /+86 15968118931.